How do Graphene Headphone Drivers Work?
Headphone drivers are arguably the most critical pieces of equipment in a headphone. They’re responsible for producing the soundwaves that reach our ears and get interpreted by our brains as music, speech, and other sounds, and over the years there have been many technological breakthroughs in headphone drivers that have pushed the standards for audio quality higher and higher. In this article, we’ll take a look at graphene headphone drivers and how they work.
This article is part of our series on headphones and headphone drivers. You can always check out our overarching article on headphone drivers in case you’re interested.
What are Graphene Drivers?
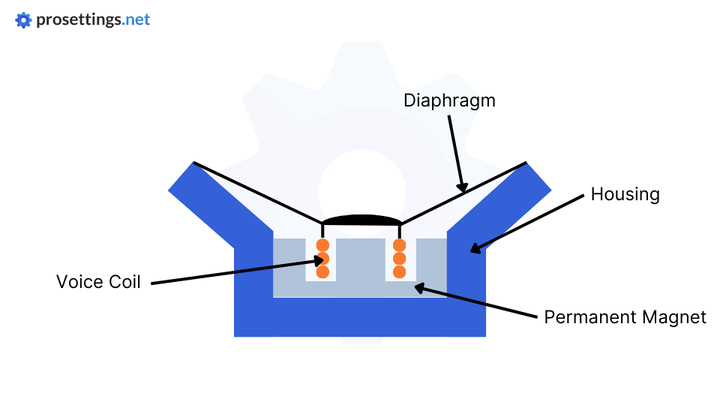
Headphone drivers are (generally speaking) made up out of three important parts:
- Magnet
- Voice coil (this is a coiled conductive wire)
- Diaphragm (a thin membrane)
In a nutshell, headphone drivers create sound by vibrating the diaphragm at frequencies that match the audio signal that’s being fed to the driver. These vibrations cause disturbances in the (air) molecules around the diaphragm, resulting in sound waves that can then reach our ears and be interpreted by our brains as music.
A traditional headphone driver (dynamic drivers are the most common headphone drivers out there at this point in time) gets the diaphragm to vibrate by attaching it to a voice coil that sits between magnets with an always present magnetic field. When an electric signal (i.e. an audio signal) then gets introduced to the voice coil, it becomes electromagnetic, causing it to be attracted as well as repulsed by the magnets around it, leading it to vibrate. This vibration also causes the diaphragm to vibrate.
Generally speaking, you’ll want the diaphragm to be as thin and light as possible. The thinner and lighter the material, the more responsive it is and the less prone it is to distortion, and thinner and lighter materials obviously also need less power to move them. A ton of different materials have been used for the diaphragm over time, and all of them have their own pros and cons but recently, and graphene is one of the newest materials to be used.
Graphene Drivers – Pros and Cons
Graphene drivers are, in essence, dynamic drivers that use graphene for a diaphragm. The usage of this atom-thick material theoretically has a number of very obvious advantages:
- It’s lightweight and requires very little power to drive, meaning that it can be used in energy-efficient (wireless) headphones
- Due to the incredibly low mass it’s very responsive and produces a great and natural sound with lots of details
- It’s less prone to distortion
All of this combined makes graphene a great material for drivers, but graphene isn’t easy to work with and as such, graphene drivers are rare in today’s market. The fact that the tech is still rather new also drives up the price and makes it so that implementing graphene drivers requires a ton of engineering know-how.
Conclusion – Graphene Drivers
Graphene drivers are an exciting prospect, and as more and more research gets devoted to using this material in audio drivers, we might see it get implemented in more audio products soon.
Within the esports space, Logitech has been a frontrunner in introducing this promising technology to their lineup. We have reviewed the Logitech G Pro X 2 LIGHTSPEED Headset here.
The world of audio never stands still, so it’s always exciting to think about what the future may hold.


